Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass.The pancreas lies behind the stomach and in front of the spine.Cancer spreads through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood.Metastasis is cancer that spreads to another part of the body.
There are two kinds of cells in the pancreas :
- Exocrine pancreas cells make enzymes that are released into the small intestine to help the body digest food.
- Neuroendocrine pancreas cells (Islet cells) make several hormones, includin insulin, gastrin, and glucagon, that help in controlling sugar levels in the blood.
The many types of pancreatic cancer can be divided into two general groups :
- Exocrine Pancreatic Cancer arises in the pancreatic ductal epithelium.It originates in the ducts that carry secretions, such as enzyme and bicarbonate away from pancreas.
- Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor arises from the body's neuroendocrine cells, which are responsible for integrating the nervous and endocrine systems.
The Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer
- Pain in the upper abdomen or back, often spreading from around the stomach to the back.
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice, a yellow tint to the whites of the eyes or skin with or without pain, and possible in combination with darkened urine
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Vomiting
- Feeling of fullness
- Weakness
- Dry mouth
- Tiredness easily
- The problem of sleeping
- Palpable abdominal mass
- Itching
- Enlarged liver and gallbladder
- Blood clots in the legs
- Mental status changes, such as a new onset of depression
- Black or bloody stool indicating bleeding from the digestive tract
The Risk Factors of Pancreatic Cancer
- Family history of pancreatic cancer
- Age
- Gender
- Ethnicity
- Obesity
- Tobacco smoking
- Diabetes mellitus
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Dietary factor (processed meat, red meat cooked by high temperature)
The pancreatic cancer symptoms at diagnosis vary according to the location of cancer in the pancreas, which anatomists divide into thick head, the neck, and the tapering body, ending in the tail.
The Tests to diagnose pancreatic cancer :
- Medical Imaging techniques include Computed Tomography scan (CT scan) and Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) are to decide whether tumor can be removed surgically (its resectability).
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a procedure that uses a magnet, radio, wave, and computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a procedure to find malignant tumor cells in the body.
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
- Abdominal Ultrasound is a procedure in which high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) are bounced off internal tissues or organs of abdomen and make echoes.
- A biopsy by fine needle Aspiration
- Liver function test is a test in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of certain substances released into the blood by the liver.
The Stage of Pancreatic Cancer :
- Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ) : Abnormal cells are found in the lining of pancreas.These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue.
- Stage IA : The tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller.
- Stage IB : The tumor is larger than 2 centimeters.
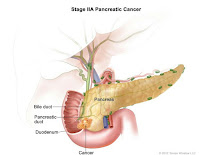
- Stage IIA : Cancer has spread to nearby tissue and organs but has not spread nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IIB : Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes and may have spread to nearby tissue and organs.
- Stage III : Cancer has spread to the major blood vessels near the pancreas.These include the superior mesenteric artery, celiac axis, common hepatic artery, and portal vein.Cancer may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV : Cancer may be any size and has spread to distant organs, such as the lung, liver, and peritoneal cavity (the space in the abdomen that contains intestines, stomach, and liver).Cancer may also have spread to tissue and organs near the pancreas or lymph nodes.
Treatment Options of Pancreatic Cancer Stage
I. The Treatment of Stage I and Stage II include
I. The Treatment of Stage I and Stage II include
- Surgery.
- Surgery followed by chemotherapy.
- Surgery followed by chemoradiation.
- A clinical trial of combination chemotherapy.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy and targeted therapy with or without chemoradiation.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy before surgery.
II. The Treatment of Stage III includes
- Palliative surgery or stent placement to bypass blocked areas in ducts or the small intestine.
- Chemotherapy folowed by chemoradiation
- Chemoradiation followed by chemotherapy
- A clinical trial of new anticancer therapies together with chemotherapy or chemoradiation.
- A clinical trial of radiation therapy given during surgery or internal radiation therapy.
III. Treatment of Stage IV includes
- Palliative treatments to relieve pain, such as nerve blocks and other supportive care.
- Palliative surgery or stent placement to bypass blocked areas in ducts or the small intestine.
- Chemotherapy with or without targeted therapy.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer agents with or without chemotherapy.
The Standard Treatments of Pancreatic Cancer
1. Surgery is to take out the tumor.
- Whipple procedure is a surgical procedure in which the head of the pancreas, the gallbladder, part of the stomach, part of small intestine and the bile duct are removed.
- Total pancreatectomy is the operation to remove the whole pancreaspart of the stomach, part of small intestine, the common bile duct , the gallbladder, the spleen, and nearby lymph nodes.
- Distal pancreatectomy is the body and the tail of the pancreas and the spleen are removed
Palliative surgery is used to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of live and is done if cancer has spread and cannot be removed.
- Surgical biliary bypass is used if the cancer is blocking the small intestine. A biliary by pass may be done if Bile is building up in the gallbladder.
- Endoscopic stent placement is used if the tumor is blocking the bile duct.Surgery may be done to put a stent (a thin tube) to drain bile that has built up in the area.
- Gastric bypass is used if the tumor is blocking the flow of food from the stomach.The stomach may be sewn directly to the small intestine in order to eat normally.
2. Radiation Theraphy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing.
Types of radiation therapy :
- External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer.
- Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive subtance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer.
3. Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or stopping them from dividing.
4. Chemoradiation therapy is the combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy to increase the effect of both.
5.Targeted Therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells.Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKIs) are targeted therapy drugs that blocks signals needed for tumors to grow.Erlotinib is a type of tyrosine kinase inhibitors to treat pancreatic cancer.
6. Biologic Therapy (Biotheraphy) is a treatment that uses the patient's immune system to fight cancer.
The Drugs for Pancreatic Cancer
- Abraxane (Paclitaxel Albumin-stabilized Nanoparticle Formulation)
- Afinitor (Everolimus)
- Erlotinib Hydrochloride
- Everolimus
- 5-FU (Fluorouracil injection)
- Fluorouracil injection
- Gemcitabine Hydrochloride
- Gemzar (Gemcitabine Hydrochloride)
- Irinotecan Hydrochloride Liposome
- Mitomycin C
- Mitozytrex (Mitomycin C)
- Mutamycin (Mitomycin C)
- Onivyde (Irinotecan Hydrochloride Liposome)
- Paclitaxel Albumin-stabilized Nanoparticle Formulation
- Sunitinib Malate
- Sutent (Sunitinib Malate)
- Tarceva (Erlotinib Hydrochloride)
Drug combinations used in Pancreatic Cancer
- Folfirinox
- Gemcitabine-Cisplatin
- Gemcitabine-Oxaliplatin
Drugs approved for Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendoctrine Tumor
- Lanreotide Acetate
- Somatuline Depot (Lanreotide Acetate)





No comments:
Post a Comment